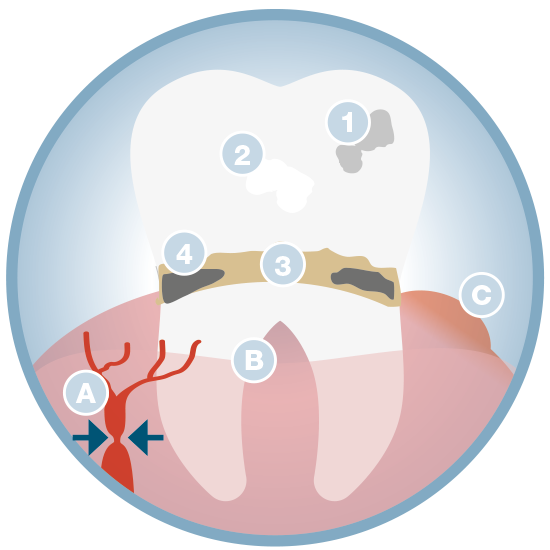
Vasoconstriction of capillaries, reducing blood flow.
Gingival recession, exposing the dental root.
Inflammation of the gums, periodontitis.
Predisposition to periodontal disease.
Risk of gingivitis 2 to 6 times higher than non-smokers.
Stains on the tooth surface.
Decalcification caused by acidity.
Increased dental plaque due to bacterial growth.
Increased caries, especially root caries.
Failure of dental implants.
-Proliferation of bacteria responsible for bacterial plaque.
-Alterations in the composition and efficacy of saliva.
-Reduced oxygen supply to tissues.
-Delayed wound healing.
-Smoker's hyalitosis.